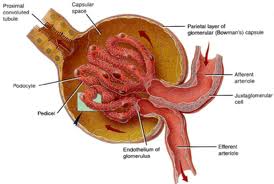
Glomerulonephritis is also known as glomerular nephritis (GN) or glomerular disease. It is a disease of the kidney, characterized by inflammation of the glomeruli. Glomeruli are very small blood vessels in the kidneys that act as tiny little filters - there are about one million glomeruli in each kidney. The disease damages the kidneys' ability to remove waste and excess fluids from the body.
GN can be acute, meaning there is a sudden attack of inflammation, or chronic (long-term and coming on gradually).
People can develop glomerulonephritis on its own, in which case it is called primary glomerulonephritis. If it is caused by another disease, such as diabetes or lupus, infection, or drugs it is called secondary glomerulonephritis.
Signs and symptoms
A symptom is something the patient feels or reports, while a sign is something other people, including the doctor may detect. For example, a headache may be a symptom while a rash may be a sign.
Some patients may not show any clear symptoms. The type of signs and symptoms will usually depend on whether it is the acute or chronic form, and its cause. For some people, their first indication that something is not right is when the results of a urine or blood sample test come back.
• Urine - if the glomeruli are damaged there will be a small amount of blood and/or protein in the urine, which may be visible or will show up in a urine test.
If symptoms are more severe the individual's urine will turn visibly red - sometimes it may be Coca-cola colored. If the urine is cloudy or frothy it means that excess protein is present (proterinuria).
A healthy adult urinates between 1 to 1.5 liters per day. People with severe glomerulonephritis may spend two or three days without being able to urinate; and when they do, there may be blood and/or protein in the urine.
• Kidney damage - in the initial stage the inflammation of the kidneys may not be evident. Symptoms may suddenly appear, or come on about three weeks after infection. Patients with glomerulonephritis caused by kidney damage may have the following signs or symptoms:
o An elevated body temperature (typically about 38C, 100.4F)
o Breathing difficulties
o Edema (swelling), especially in the hands, face, feet, ankles or abdomen
o Loss of appetite
o Nausea
o Pallor
o Vision problems
o Vomiting
The following signs or symptoms are also possible:
o Hypertension (high blood pressure)
o Fatigue
• Kidney pain - although pain in the kidneys is possible, it is unusual. When pain is felt, it is usually in the upper back, behind the ribs. Sometimes the pain may be intense. Kidney pain might be a symptom of kidney stones or a kidney infection, instead of glomerulonephritis.
No comments:
Post a Comment